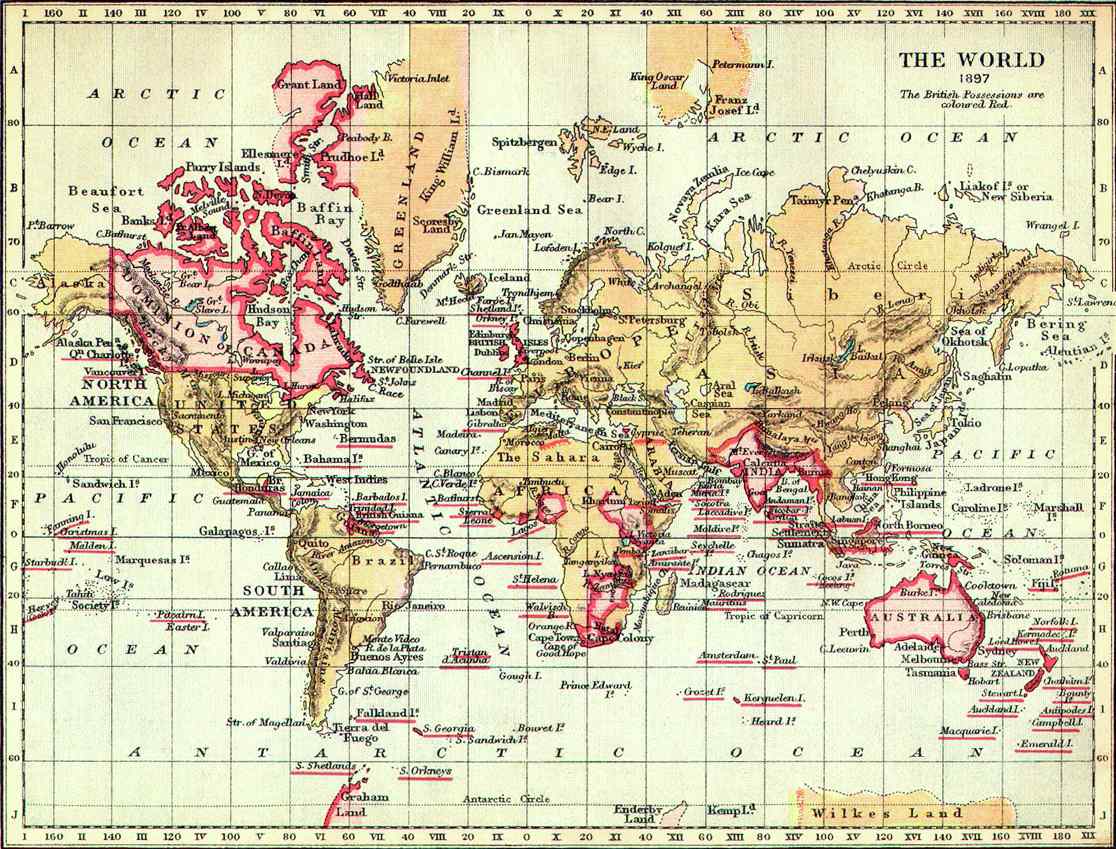
THE BRITISH EMPIRE
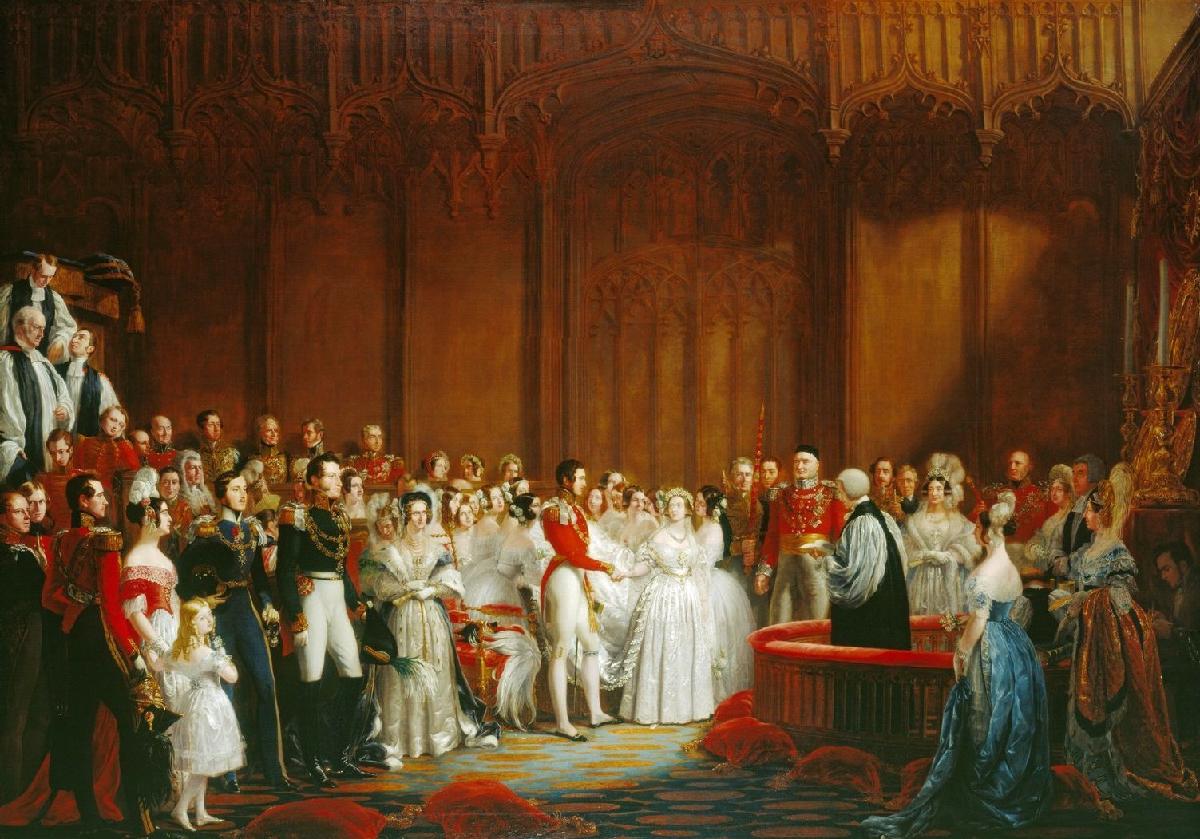

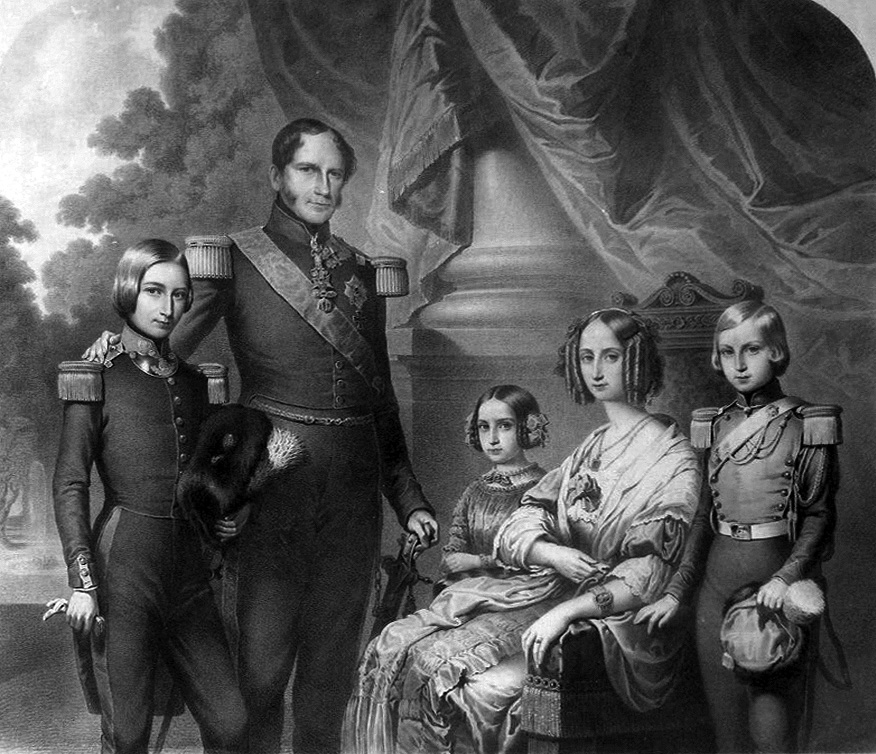
The Marriage of Queen Victoria,
10 February 1840 – by Sir George Hayter (1840-1842)
Wikipedia - "Victoria
of the United Kingdom"
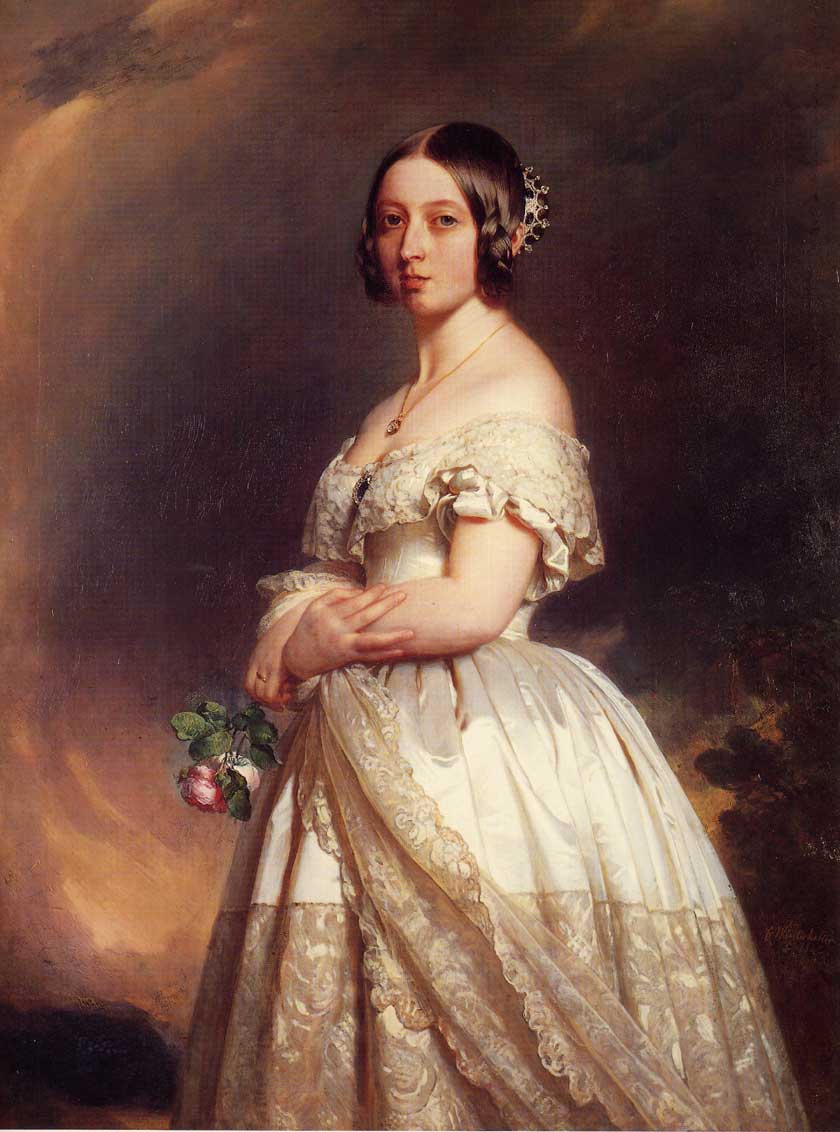
Queen Victoria (1819-1901)
– Franz Xaver Winterhalter - 1842
The longest reigning
monarch in the United Kingdom (1837-1901)
Osborne House, Isle of Wight
Wikipedia - "Victoria
of the United Kingdom"
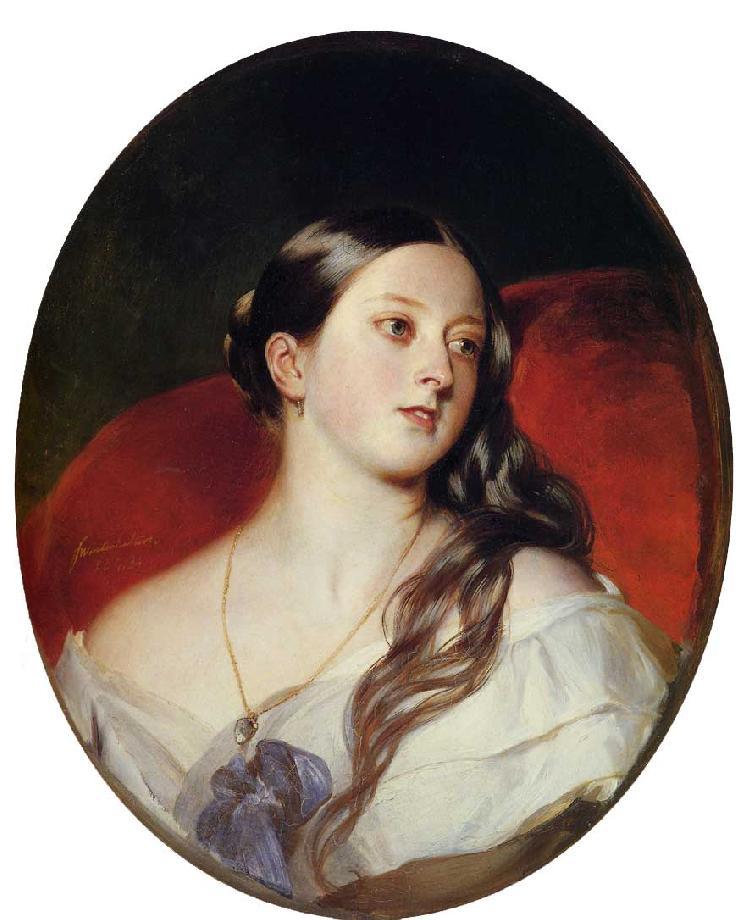
Queen Victoria –
Franz Xaver Winterhalter - 1843
Wikipedia - "Franz
Xaver Winterhalter"
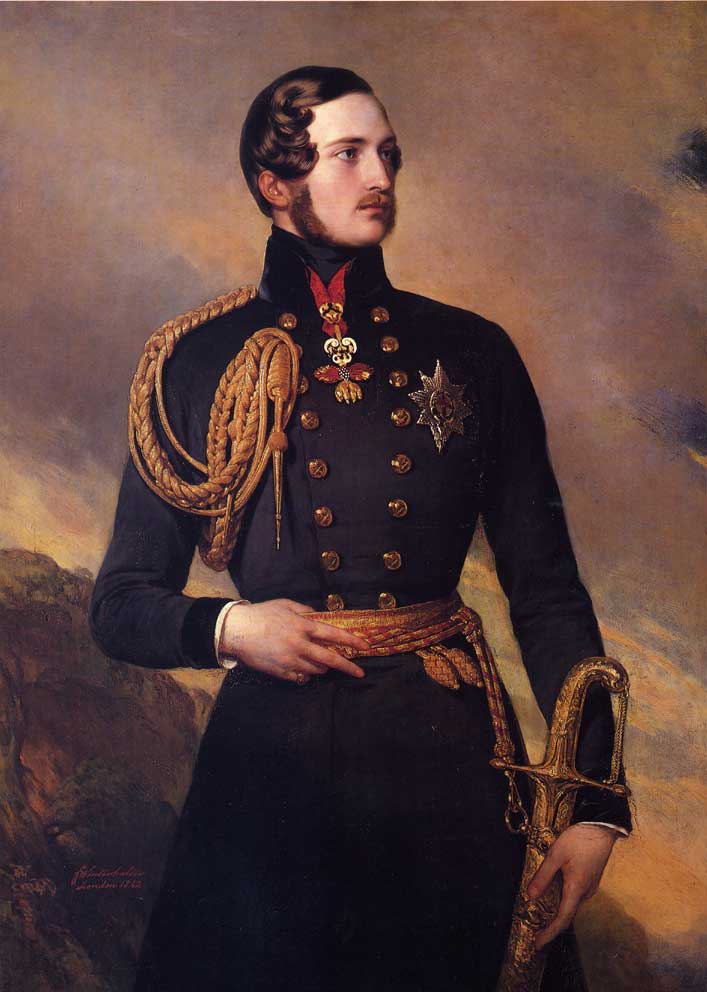

Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg
and Gotha – Franz Xaver Winterhalter - 1842
Prince Consort 1819-1861
Wikipedia - "Franz
Xaver Winterhalter"

Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg
and Gotha – Franz Xaver Winterhalter - 1846
Lady Lever Art Gallery,
Port Sunlight
Wikipedia - "Franz
Xaver Winterhalter"
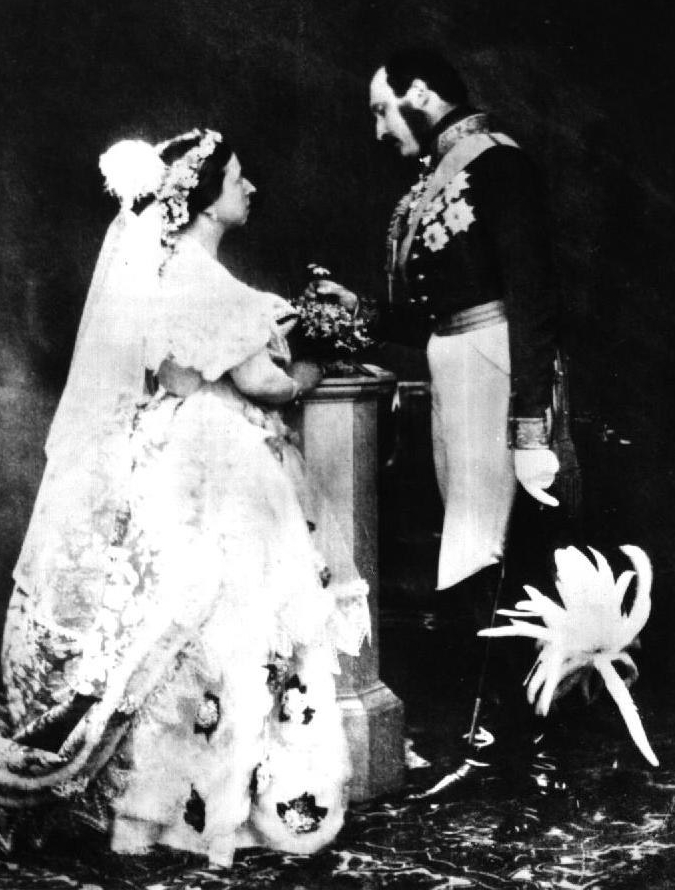

Queen Victoria and Prince
Albert – possibly recreating a wedding pose for the newly developed
art form of photography (ca. 1854)
Wikipedia - "Victoria
of the United Kingdom"

Queen Victoria –
Photo by Alexander Bessano (1887)
Wikipedia - "Victoria
of the United Kingdom"

Queen Victoria –
Photo by Alexander Bessano (1887)
Wikipedia - "Victorian
era"

Queen Victoria –
Diamond Jubilee - 1897
Wikipedia - "Victoria
of the United Kingdom"
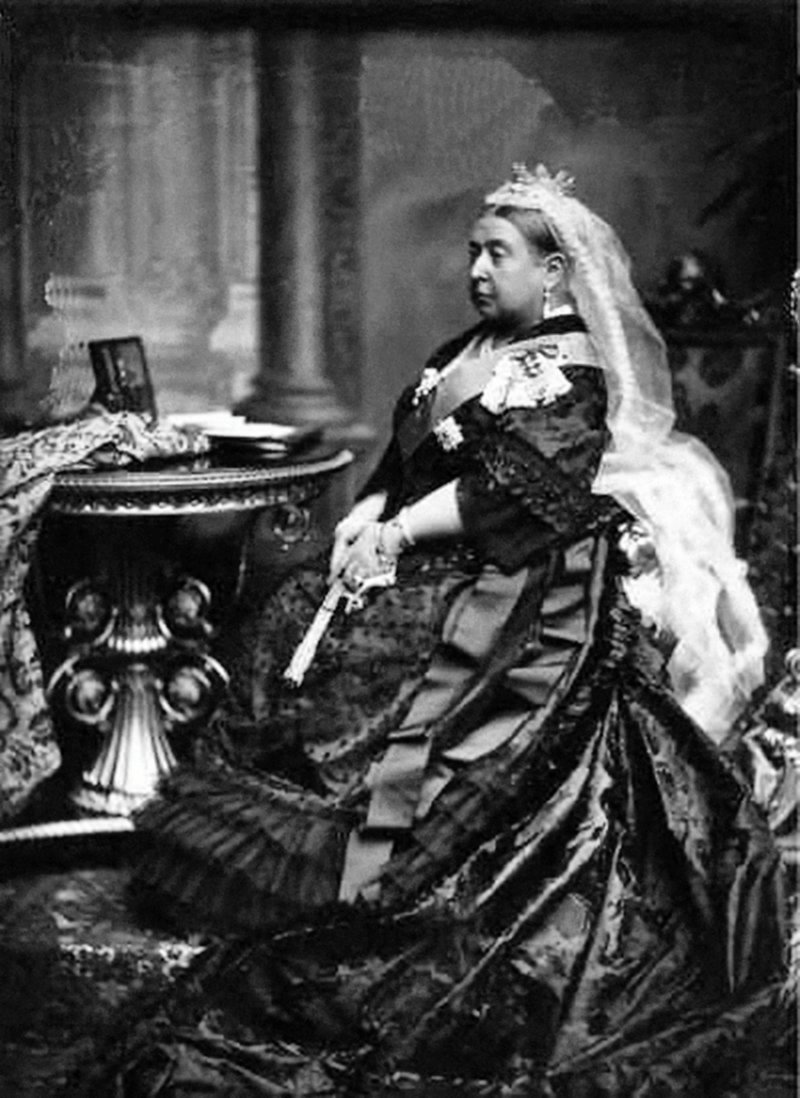

Queen Victoria
Wikipedia - "History
of the United Kingdom"
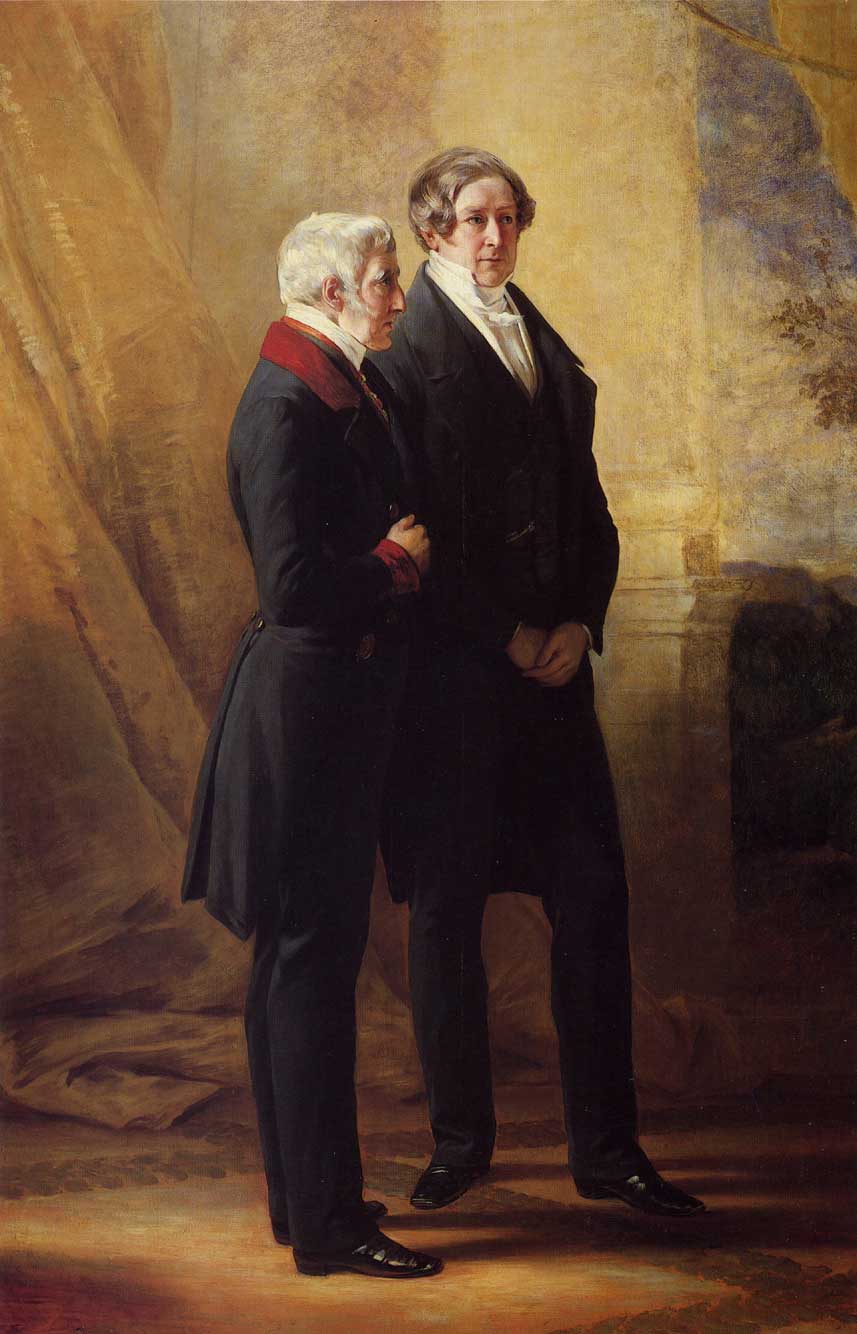

The Duke of Wellington and
Sir Robert Peel - 1844
Wikipedia - "Franz
Xaver Winterhalter"

Henry John Temple, 3rd Viscount
Palmerston
Whig/Liberal Prime Minister
of the United Kingdom – 1855-1858, 1859-1865.
Foreign Secretary
– 1830-1834, 1835-1841, 1846-1851
Wikipedia - "Henry
John Temple, 3rd Viscount Palmerston"
![]()
English Prime Minister Benjamin
Disraeli
Prime Minister of the United
Kingdom – 1868 & 1874-1880.
Wikipedia - "Benjamin
Disraeli"
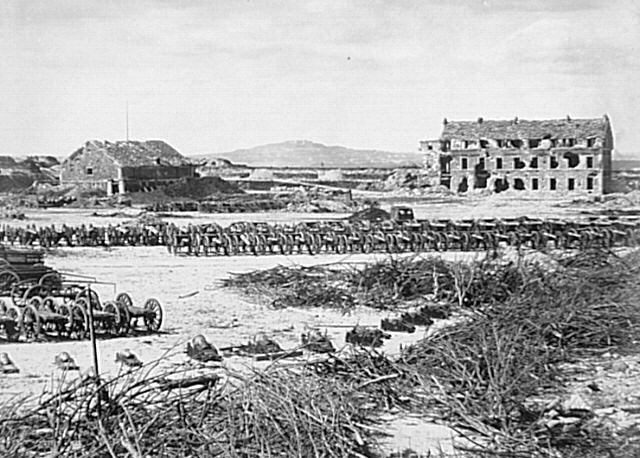
British India
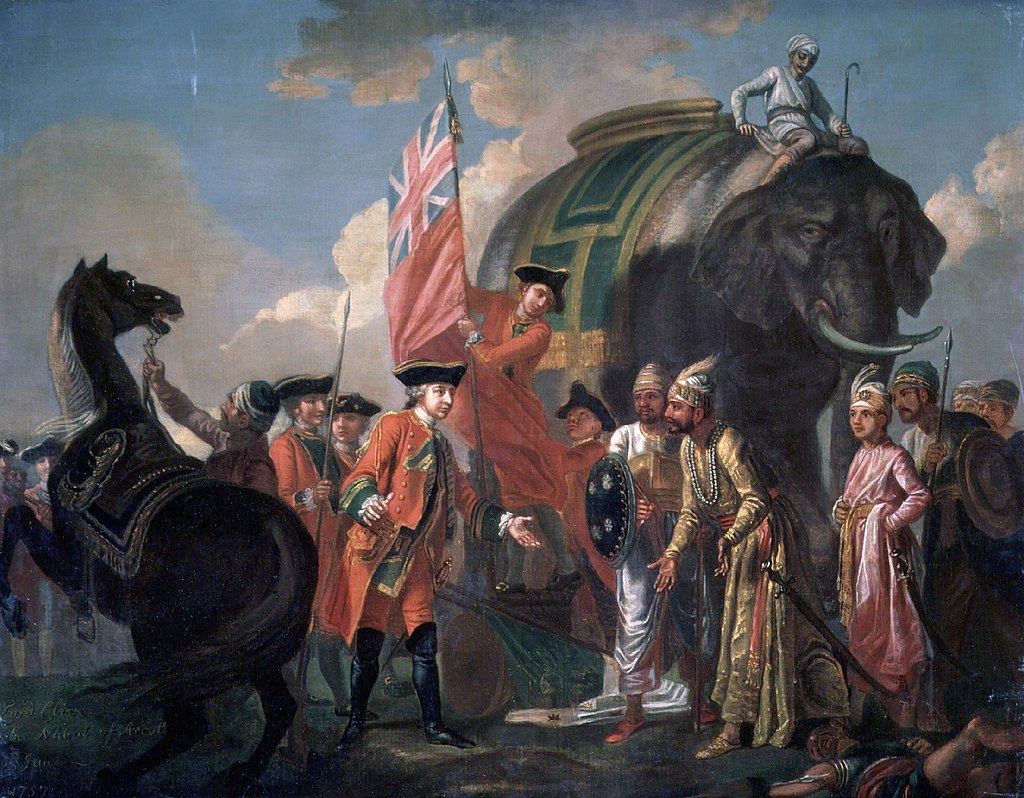

Lord Clive meeting with Mir
Jafar after the Battle of Plassey - by Francis Hayman (c. 1762).
Robert Clive, 1st Baron
Clive, first British Governor of Bengal (India)
Robert Clive's victory at
the Battle of Plassey established
the Company as a military
as well as a commercial power.
Wikipedia - "British
Empire"
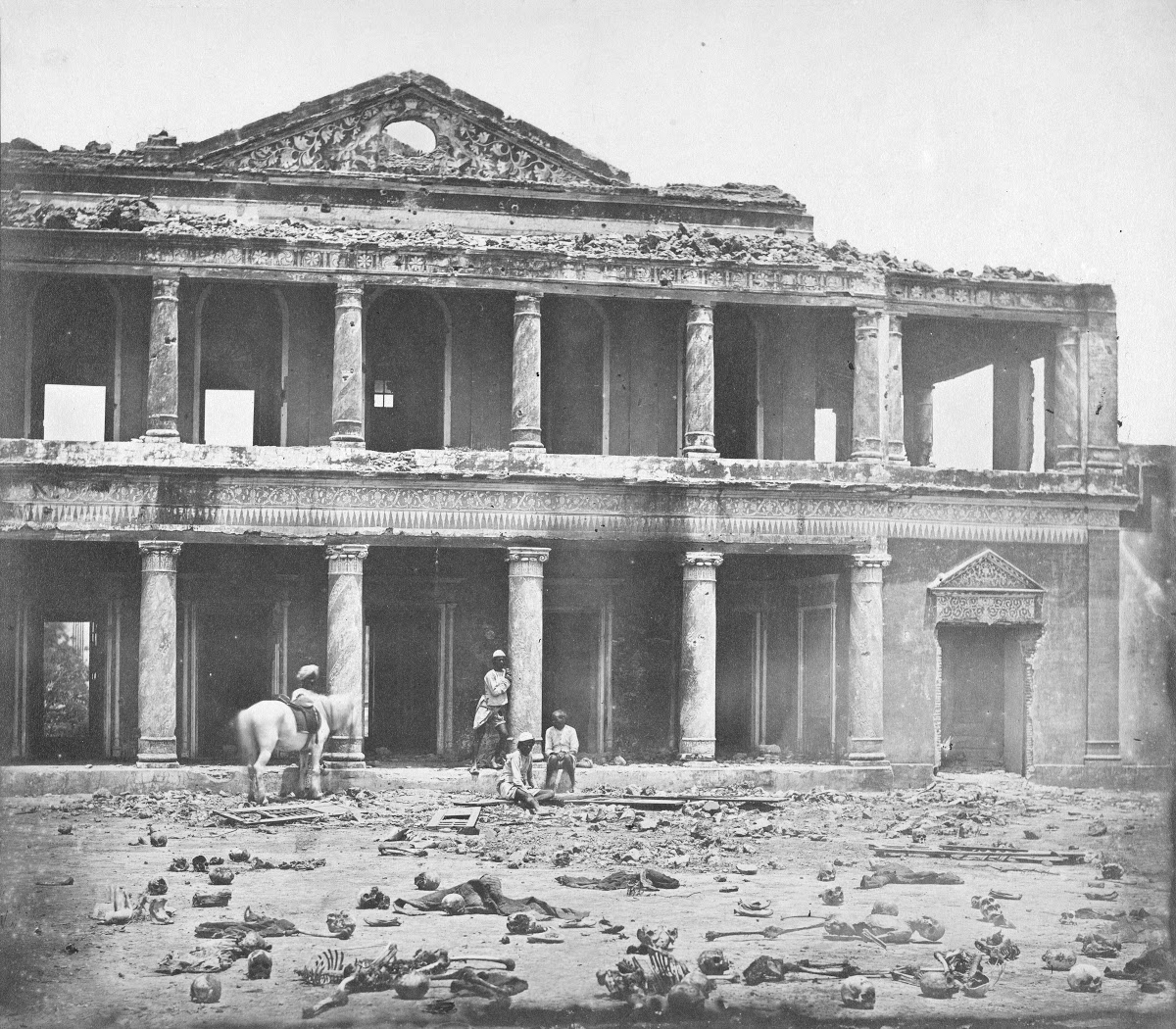
The Sepoy Mutiny in India
(1857-1858)
and the British Crown's
takeover of India from the East India Company